Agentic AI vs. Reactive AI: An Expert’s View on the Evolving Landscape
This blog explores the key differences between Agentic AI vs Reactive AI. Reactive AI follows fixed rules for specific tasks, while Agentic AI is more autonomous, learning and adapting over time. Check out how Agentic AI is driving innovation, while Reactive AI remains crucial for predictable, rule-based applications. Both are shaping the future of technology and raising ethical questions.
Introduction
The AI world is becoming dynamic and evolving at a breathtaking pace, reshaping industries and daily life as it is essential to understand the types of AI systems that are leading the change. Agentic and Reactive AI are two categories at the two ends of the AI with distinctive benefits, drawbacks, and potential.
Reactive AI offers pre-defined actions in response to a given set of situations, however, Agentic AI goes one step further by having responses that are self-generated. But what makes them different, and why does this differentiation become important as we move into an AI-intensive future?
In this expert’s view, we’ll look through their fundamental differences and the impact they have on both society and technology. Thus, irrespective of where one is on the developmental spectrum – from an industry giant absorbed with the bearings of AI to the developer to be stimulated and challenged by its dynamic expansion, knowledge of the distinctions between Agentic and Reactive AI will extend profound perspectives into the future.
For businesses seeking to develop next-gen AI, working with a top-notch and forward-thinking AI development company can be your next move because their expertise and innovation will help to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI systems possess a high degree of autonomy and decision-making capability. Unlike traditional AI models that operate on pre-programmed rules or simple responses to input, Agentic AI can act independently, adapt to new situations, make decisions, and learn from experiences without any human intervention.
Such systems are created to ease the tasks that require reasoning, judgment, and planning, just like human agents do.
For instance, an Agentic AI might be a self-driving car where the car AI has the authority to decide and act on certain choices, such as where to go, how to avoid an accident, or how to react to changes on the road.
Agentic AI differs from reactive AI in the sense that it is capable of developing over time, adapting, and even inventing new routines based on data it receives over time, making it more dynamic than simpler reactive systems.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI:
- Autonomy: It can act independently and make effective decisions.
- Adaptability: Evolving and learning by interacting with the environment.
- Decision-making: Can conduct complicated cognitive operations such as planning, prioritizing, and reasoning.
- Context awareness: It reacts and understands a broad set of information and situations.
What is Reactive AI?
On the other hand, Reactive AI is a simpler AI system that responds to specific inputs with pre-defined actions. It should be noted that, unlike Agentic AI, Reactive AI has limited control, and does not display higher-order decision-making or learning.
Reactive artificial intelligence is applied when it is necessary to achieve a specific goal through a fixed number of responses, without change, learning, or self-development; its purpose is to accomplish specific assigned tasks and fulfill routine operations following rules.
Reactive AI is an application where an entity interacts with stimuli and produces a predetermined response like a chatbot that might respond to customer queries with a set reply or a recommender system that might recommend products based on the customer’s previous purchases.
Reactive AI does not respond to the new data in a passive-active manner; it only responds to what is presented to it at a particular time.
Key Characteristics of Reactive AI:
- Rule-based: It performs on predefined algorithms and responses.
- Limited adaptability: It cannot change behavior unless you manually update it.
- Simple decision-making: Based on pattern recognition, the responses are made rather than learning and reasoning.
- Context dependency: It immediately reacts to stimuli, but does not consider broader context and long-term implications.
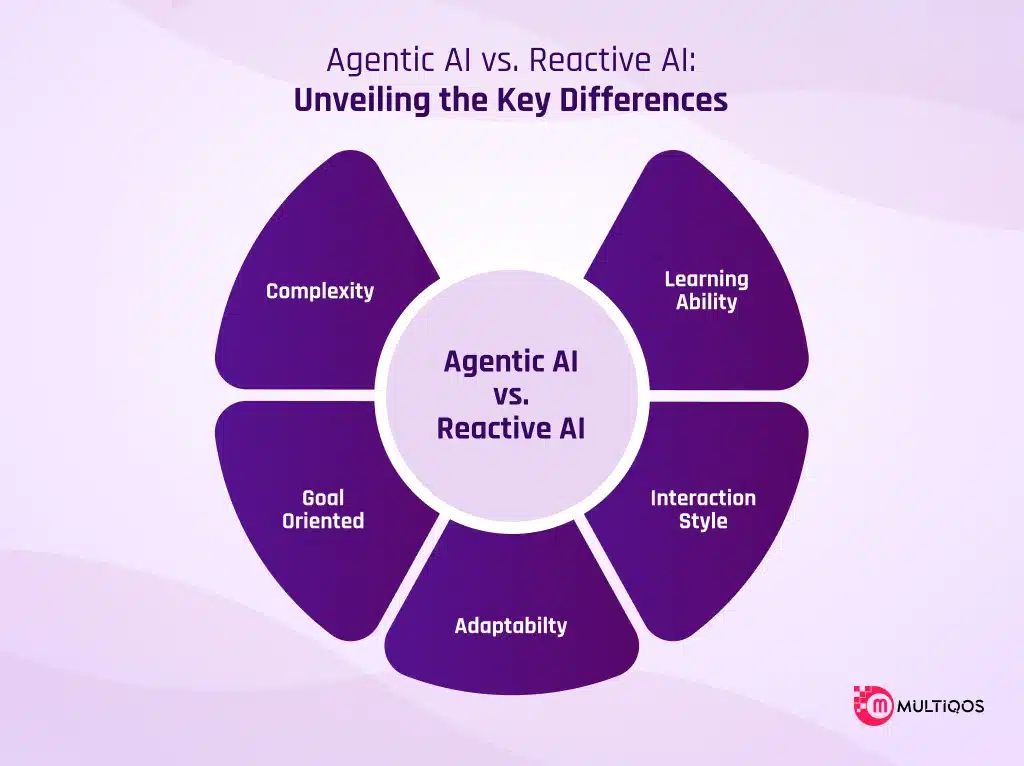
Comparing Agentic AI vs. Reactive AI
| Aspect | Agentic AI | Reactive AI |
| Complexity | Goal-setting abilities, self-learning, and decision-making make it complex to learn. | Simple as compared to Agentic AI, as Reactive AI mainly focuses on predefined responses or patterns. |
| Goal-Oriented | It is goal-oriented because Agentic AI works for long-term goals and plans accordingly. | It is not goal-oriented because Reactive AI works based on immediate, reactive responses to stimuli. |
| Adaptability | High adaptability; it adjusts various strategies and behavior depending on the situation. | Low adaptability; the behavior is static based on predetermined responses. |
| Interaction Style | Agentic AI engages in interactive decision-making and dynamic processes with users. | Reactive AI follows specific commands to fixed triggers without deeper interaction. |
| Dependency on Data | Might need a massive amount of data to refine its objectives and strategies. | Might work with limited data when it comes to performing repetitive tasks. |
| Learning Ability | Agentic AI adapts and learns from experiences, improving with time. | Learning is limited as it is reliant mostly on pre-programmed patterns or rules. |
| Contextual Awareness | High because it understands the context and adjusts actions based on the context. | Limited because it responds mainly to inputs without contextual understanding. |
| Examples | AI in robotics, autonomous vehicles, and advanced chatbots that plan tasks and resolve problems. | Traditional expert systems, spam filters, and simple voice assistants. |
Agentic AI vs. Reactive AI: Comparing the Differences In Detail
1). Complexity:
Agentic AI:
- High-Complexity: Agentic AI is created using the latest techniques such as reinforcement learning, deep learning, and neural networks. These systems have to use huge computing resources to parse through large data sets, learn from experience or previous data, and plan how to do future tasks.
- Requires Extensive Training: These models depend on large amounts of data to get specific in fine-tuning organizational decision-making modes to properly establish long-term objectives and to act towards their achievement.
Reactive AI:
- Low to Moderate Complexity: Reactive AI is generally less complex than Agentic AI and will often use algorithmic procedures, decision-based rules, or a decision tree. It produces very limited learning in its operation.
- Fixed Responses: It responds according to predetermined patterns or patterns the workload of the system is much lower in comparison to the agentic systems.
2). Goal-Oriented:
Agentic AI:
- Proactively Goal-Oriented: It has the ability to establish, modify, and strive towards goals by itself. Self-driven AI can determine the strategies that will enable one to attain long-term goals and essentially assess the environment for the best approach.
- Long-Term Planning: Agentic AI executes a series of actions apart from just focusing on the immediate task over an extended period to accomplish complex objectives.
Reactive AI:
- No Long-term Goal Setting: It is mainly responsive to external stimuli without consideration of broader goals and there are no plans or pre-defined objectives beyond the current reaction.
- Immediate Task Focused: Reactive AI is best applied where the inputs and outputs are clearly defined for strategic thinking or future planning.
3). Adaptability:
Agentic AI:
- High Adaptability: Agentic AI will be able to assess the situation and produce the replies that correspond to it. It can adapt to just about anything from a different environment or new challenges that can change its behavior to suit the situation.
- Content-Aware: The ability of these systems is that they can analyze a slight change in environment and can adapt the decision-making procedure correspondingly.
Reactive AI:
- Low-Adaptability: Reactive AI cannot change or learn with new developments. It usually produces the same type of response to a given situation, even if the conditions of the environment are different.
- Content-Limited: It simply behaves with its predefined responses without a real-time adjustment to a new context or any information.
4). Interaction Style:
Agentic AI:
- Dynamic-Interaction: Engages in a complex form of interaction negotiation is done by AI and it adjusts responses based on recent exchanges and the latest data.
- Decision-Making: Decision-making is actively focused while interacting and might ask to clarify queries or adapt its responses based on the latest context.
Reactive AI:
- Static-Interaction: Reactive AI systems work in a manner where the system always follows a pre-planned output for a given input. They do not change their behavior during the act of interacting with each other.
- Response-Based: The interaction is usually set for a specific pattern and replies to predefined commands or questions.
5). Learning Ability:
Agentic AI:
- Learning and Adaption: Agentic AI is capable of learning from experiences; its behavior changes with new data input. They include: reinforcement learning which enables it to solve for strategies and actions that require constant optimization.
- Continuous Improvement: The system can develop and adapt over time as it compiles more data and appeals to different situations in which it will then be more efficient at reaching the intended goals.
Reactive AI:
- Limited or No-Learning: Reactive AI does not reciprocate that it has even made an action or learned from previous events. Usually, it has a set of highly structured algorithms developed by human experts and thus behaves in a certain pre-designated way until the change is made by its user.
- Static Operation: It does not adapt or change its process in any way after the previous run, manually coded to address new tasks.
The Road Ahead: What’s Next for AI Development?
There exists an inevitable prospect of AI development in the future, and specific areas of development such as AGI, self-automated systems, and medicine. As AI advances we may get the creation of AGI that will go beyond specific usage domains to encompass a spectrum of general activities, replicating human-level intelligence.
However, as these technologies advance managing the ethical issues in private life, security, and automation in society will be important.
At the same time, progress in creating AI will prompt questions about its regulation and governance. Making sure that AI systems are transparent and fair will be crucial as they are deployed in major areas such as fintech, healthcare, and criminal justice.
The concern for AI’s accountability will increase, with governments and organizations operating to establish regulations to ensure that artificial intelligence serves positively without reinforcing inequalities and biases.
The future for AI is bright but it has a lot of challenges it needs to overcome it has never been so promising for these technologies to be developed and introduced to help humanity with the desire for worth while bearing in mind the ethical challenges it has.
Conclusion
The comparison between Agentic and Reactive AI defines the development of artificial intelligence, the capacity to think, learn from experience, and act accordingly constituting the future AI environment. While Reactive AI is still incredibly successful at managing pre-planned tasks, on the other hand, Agentic AI activates change, goal, and adaptability.
Advancements in AI and application development services are endless, and we’re likely to see a transformation from rule-based reactive systems to more complicated agentic models that can perform a variety of functions and change in response to real-world dynamics.
However, such progress must establish objectives and questions concerning ethical evolution, transparency, and regulation. Understanding these differences between the two categories of AI will go a long way in addressing the management of the various fields in which AI will be used and ensuring that the development of AI will be for the betterment of the population.
People Also Ask
Autonomous AI refers to a system that possesses the capability and authority to initiate goals, select courses, and execute goals independently together with adaptation. There is the Reactive AI which simply responds to certain stimuli following a set of instructions and cannot even adapt or change based on past experiences.
No, it does not evolve on its own as it works based on a fixed series of rules and cannot adapt to new data unless it is manually updated by humans.
AI is gradually moving toward more self-governed and adaptive systems that are best represented by Agentic AI. Future advances in fields of model improvements such as reinforcement learning and neural networks are expected to provide AI with the capacity to set goals for long time intervals, improve from prior experiences, and make substantial decisions across a variety of contexts.
While Reactive AI can be part of complex systems, it is limited in its ability to handle dynamic, unpredictable situations. It is best suited for environments where tasks are well-defined and responses are straightforward, but it cannot adjust to new scenarios without reprogramming.
Get In Touch