Understanding the Core Concepts of Observability in Enterprise Software
Summary:
Observability in enterprise software is essential for ensuring system reliability, performance, and scalability. It provides deep visibility into complex applications by integrating metrics, logs, and traces to identify and resolve issues proactively. Unlike traditional monitoring, observability offers a holistic view of system behavior, enabling teams to understand why failures occur, not just where.
This approach empowers enterprises to maintain high uptime, optimize performance, and enhance user experiences. By embracing observability, organizations can streamline operations, improve incident response, and build more resilient software systems that adapt to evolving business and technical demands.
Introduction
Maintaining accuracy and performance in large-scale systems is a supreme priority for businesses. Observability in enterprise software has centered as an essential practice that helps organizations achieve complete visibility into their systems’ inner workings. By linking metrics, logs, and traces, observability enable development teams to detect, analyze, and resolve issues faster.
It goes further than standard monitoring by providing usable clarity into operation approach, dependencies, and performance bottlenecks. With efficient observability frameworks in place, companies can confirm endless user experiences, reduce downtime, and establish informed decisions to optimize software performance.
What is Observability in Enterprise Software?
Observability in enterprise software refers to the ability to measure, monitor, and study the internal workings of a step in real-time to validate its performance, authenticity, and body. It involves receiving and studying data from various sources, such as logs, metrics, and traces, to provide deep insights into how the procedure is behaving.
With strong observability practices, organizations can speedily detect variations, identify the root cause of issues, and streamline troubleshooting, superior in faster resolution times and enhanced user experiences. Observability is beyond a pivotal component of enterprise software development, helping teams develop more reliable and maintainable systems from the ground up. In a company environment, observability helps bridge the gap in relation to advancement, operations, and backup teams by offering a clear, data-driven view of method conduct.
By leveraging up-to-date tools like distributed tracing, log aggregation, and digitized alerting, businesses can take achievable viewpoints that help optimize performance, manage proficiency, and predict proficiency failures ahead of they repercussion conclusion users. This proactive method of operation monitoring uplifts truth, reduces downtime, and ensures smoother scaling as organizational systems grow.
3 Pillars of Observability
The three pillars of observability in enterprise software are metrics, logs, and traces, form the foundation for understanding and maintaining complex enterprise systems. Together, they provide deep visibility into application performance, helping teams quickly detect issues, find root causes, and improve reliability.
Metrics
Metrics are numerical indicators that measure system health and performance, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, latency, and error rates. They help identify trends, detect anomalies, and set up alerts to catch problems early before they impact users.
Logs
Logs are detailed, timestamped records of events or actions within a system. They provide rich context for debugging, allowing engineers to trace specific errors or behaviors. Logs are essential for understanding what happened and why, especially during incidents.
Traces
Traces show the path of a request as it flows through various services, highlighting dependencies and performance bottlenecks. In distributed or microservices architectures, tracing is crucial for pinpointing where slowdowns or failures occur.
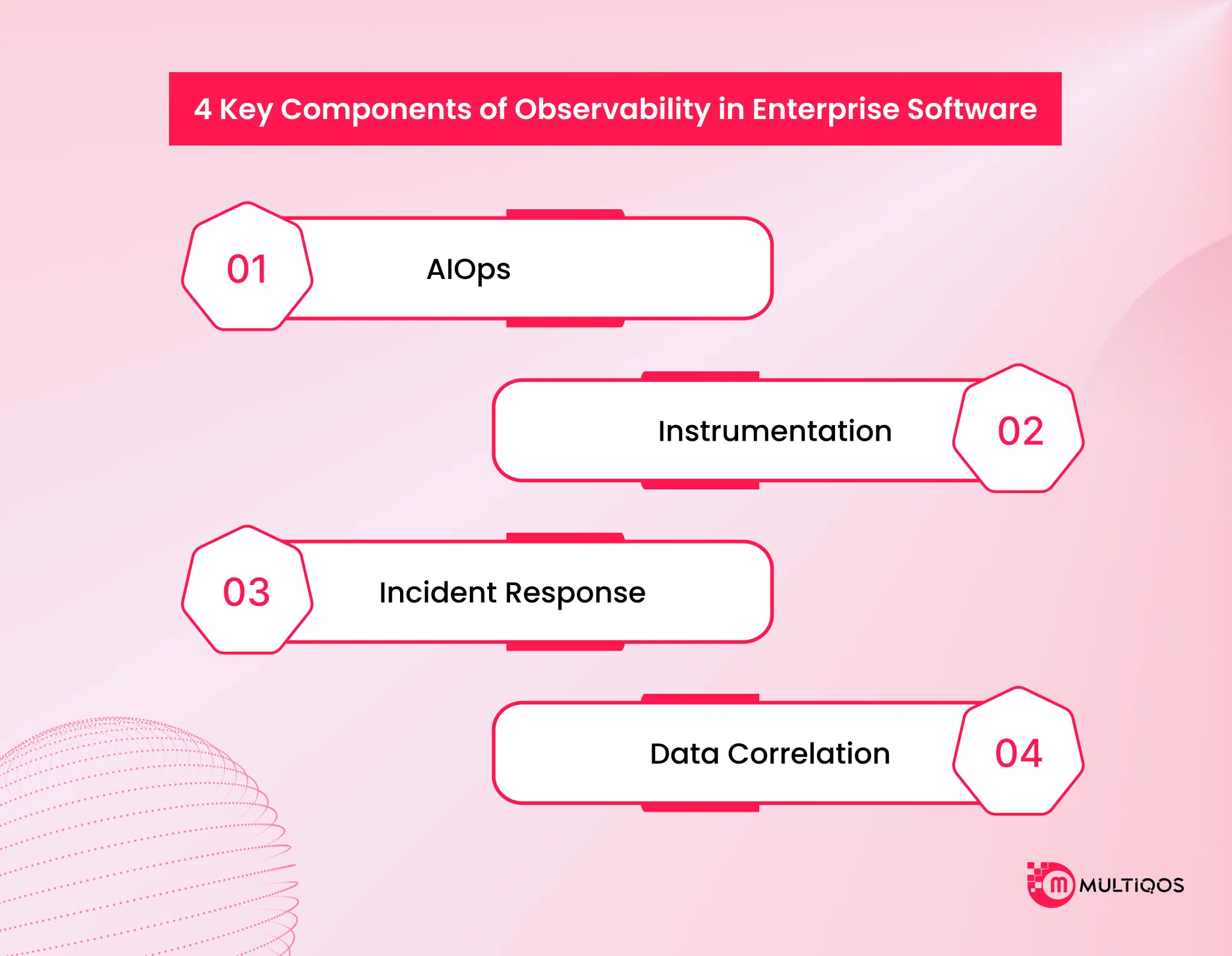
4 Key Components of Observability in Enterprise Software
The four key components of observability in enterprise software- AIOps, Instrumentation, Incident Response, and Data Correlation- work together to provide deep visibility, faster problem resolution, and improved system reliability. These components enable organizations to proactively manage complex systems and ensure optimal performance.
AIOps
AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) uses machine learning and data analytics to automate the detection, analysis, and resolution of IT issues. By processing vast amounts of observability data, AIOps can identify patterns, predict potential failures, and reduce alert noise, helping teams focus on critical incidents and improve operational efficiency.
Instrumentation
Instrumentation involves embedding monitoring tools and agents within applications and infrastructure to collect real-time data such as metrics, logs, and traces. It ensures that every component of the system is observable, enabling teams to track performance, detect anomalies, and understand how different services interact.
Incident Response
Incident response focuses on how teams detect, investigate, and resolve system issues. Effective observability streamlines this process by providing actionable insights and automated alerts, allowing teams to respond quickly and minimize downtime. It also supports post-incident analysis to prevent recurrence.
Data Correlation
Data correlation connects insights from multiple observability sources, metrics, logs, and traces to form a unified understanding of system behavior. By correlating data across layers and services, teams can uncover root causes faster and gain a holistic view of performance and dependencies.
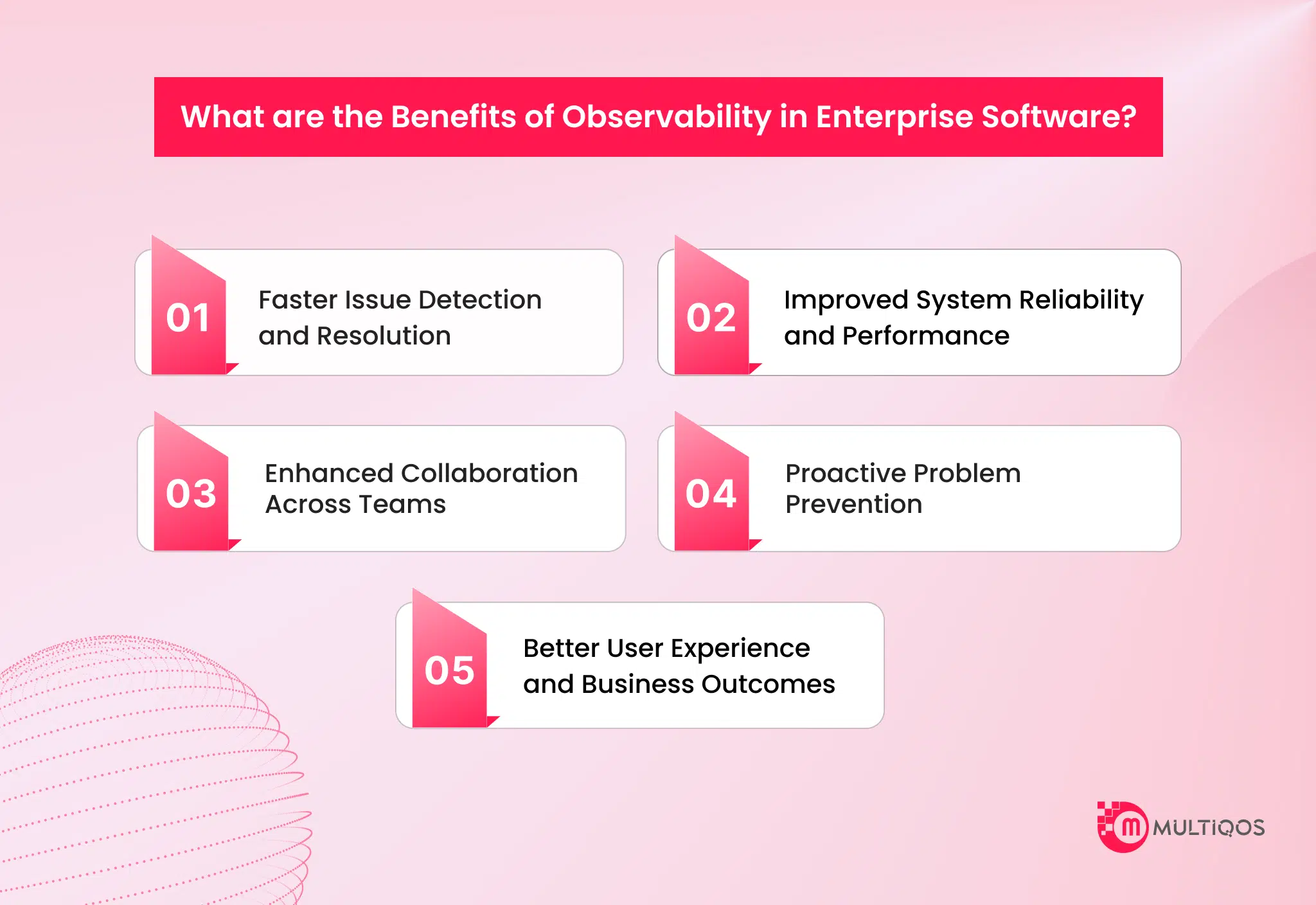
What are the Benefits of Observability in Enterprise Software?
Implementing observability in enterprise software offers organizations valuable insights that improve system performance, reliability, and overall business outcomes. Here are the key benefits:
1. Faster Issue Detection and Resolution
Observability in enterprise software allows teams to quickly detect anomalies, trace issues to their root cause, and resolve them efficiently. With real-time insights from metrics, logs, and traces, IT teams can reduce mean time to detection (MTTD) and mean time to resolution (MTTR), minimizing service disruptions and improving operational stability.
2. Improved System Reliability and Performance
Continuous monitoring and deep visibility into system components enable organizations to maintain high reliability. Observability in enterprise software helps identify performance bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and ensure that applications run smoothly even under heavy workloads.
3. Enhanced Collaboration Across Teams
Observability in enterprise software provides a unified view of data that bridges the gap between development, operations, and support teams. By sharing actionable insights, it fosters better collaboration and speeds up the decision-making process within DevOps and SRE environments. MultiQoS’s DevOps solutions integrate observability to streamline workflows and improve team efficiency.
4. Proactive Problem Prevention
With predictive analytics and intelligent alerting, observability empowers teams to detect early warning signs and potential failures before they impact users. This proactive approach helps prevent outages, reduce downtime, and ensure business continuity.
5. Better User Experience and Business Outcomes
Reliable and high-performing enterprise applications lead to a smoother user experience. Observability ensures that systems deliver consistent performance, which improves customer satisfaction, strengthens trust, and drives better overall business results.
List of Top Observability Tools
To effectively implement observability in enterprise software, organizations rely on specialized tools that provide deep insights into metrics, logs, and traces. Here are some of the top observability tools available today:
| Tool | Pros |
Cons |
|
Datadog |
Unified metrics, logs & traces; strong integrations; AI alerts | Expensive at scale; learning curve; vendor lock-in |
|
New Relic |
Full-stack observability; user-friendly UI | Costs increase with scale; less flexible than open-source |
|
Dynatrace |
AI-driven root cause analysis; automatic discovery | High cost; steep learning curve; proprietary instrumentation |
|
Elastic Observability (ELK) |
Open-source, strong log analytics, flexible | Setup & scaling can be complex; lacks full-stack automation |
|
Grafana |
Excellent visualization; open-source; flexible dashboards | Needs extra tools for full observability; alerting setup required |
|
IBM Instana |
Automatic instrumentation; full-stack coverage | Premium pricing; smaller community; requires training |
Conclusion
Observability in Enterprise Software is more than just a technical capability; it’s a strategic advantage that empowers organizations to build reliable, high-performing, and scalable systems. By leveraging observability tools and practices, enterprises can proactively identify issues, streamline workflows, and enhance system stability.
To fully harness its potential, it’s essential to collaborate with experts who understand both software architecture and modern observability frameworks. If you’re looking to strengthen your systems with advanced observability and performance insights, it’s time to hire software developers who can implement the right observability solutions tailored to your enterprise needs.
FAQs
Observability is crucial for enterprises because it enables proactive system management. It helps IT and DevOps teams quickly detect, diagnose, and resolve issues before they impact users. With complex distributed systems and microservices, observability ensures seamless operations, minimizes downtime, and improves business resilience.
Monitoring focuses on tracking known issues and predefined metrics, while observability provides deeper visibility into unknown or unexpected problems. Monitoring tells you something is wrong; observability helps you understand why it’s wrong and where it’s happening.
AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) enhances observability by using machine learning to analyze vast amounts of operational data. It identifies patterns, predicts failures, and reduces alert fatigue through intelligent automation, helping teams focus on critical issues and make faster decisions.
If you’re ready to enhance your system reliability and performance through observability, our team can help. We offer tailored solutions for metrics, logging, tracing, and AIOps integration to fit your enterprise needs. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and discover how observability can transform your IT operations and business outcomes.
Get In Touch