
Table of Content:
- Introduction
- What Is an AI Agent?
- Why Real-World AI Agent Examples Matter?
- Real-World AI Agent Applications by Industry
- How AI Agents Work: The Inner Mechanics
- Challenges in Implementing AI Agents
- The Future of AI Agent Development
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Summary:
In this article we demonstrate real AI agent examples, which apply to different domains and are employed in real world. You will also discover how these intelligent agents work, adapt, and make decisions, from self-driving cars and smart assistants to AI-supported customer service and logistics management.
Whether you’re a beginner in AI or business, or just interested in learning about AI agent development, this editorial explains the basics and technology behind the most successful AI agents out there today.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence agents are changing the process in which machines perceive, react, and learn in complex environments. AI agents are no longer the stuff of science fiction from cell phone assistants to self-driving cars, we’ve already started living our lives alongside them. But what are these agents, and how do they operate in real life?
In this article, we will go deeper into real-world AI agent examples, some basics such as AI agent definition, decision-making processes, and goal-driven behavior in AI agent development.
What Is an AI Agent?
Before diving into real-world examples, let’s establish a foundational AI agent definition. An Artificial Intelligence agent is a software-based entity that receives inputs or perceptions from its environment, processes that information, and then takes action through actuators to influence that environment—typically in pursuit of a specific goal. This goal-oriented behavior is what defines the core of intelligent autonomy.
Understanding this principle is crucial not only for theoretical knowledge but also for building practical solutions through modern AI development services, which often focus on designing such agents to perform tasks across industries with speed, accuracy, and adaptability.
So, what does an AI agent do? It receives data, does something with it, and then takes some decision according to identifiable rules or learned experiences. Such agents may be relatively simple, e.g., rule-based bots, or quite sophisticated, for instance autonomous drones that perform real-time navigation.
When talking about AI agent vs intelligent agent, people use these words as synonyms. It can also be the case that “intelligent agent” is used more generally to refer to any agent that has cognitive features including both learning and reasoning, whereas an ”AI agent” uses AI to enable such features.
Why Real-World AI Agent Examples Matter?
Examples of AI agents in the real world illustrate the connection between a highly abstract theory and its practical application. With the increasing advance of AI agent development in different application domains, these examples make clear the way AI-based agents are being developed, deployed, and managed in complex systems.
These are also just some examples to demonstrate why and how AI agents are a key to modern tech, in that they make work more productive, decrease human error, and help ensure scalable automation.
Real-World AI Agent Applications by Industry
Let’s explore real-life examples of AI agents and understand their internal logic and architecture.
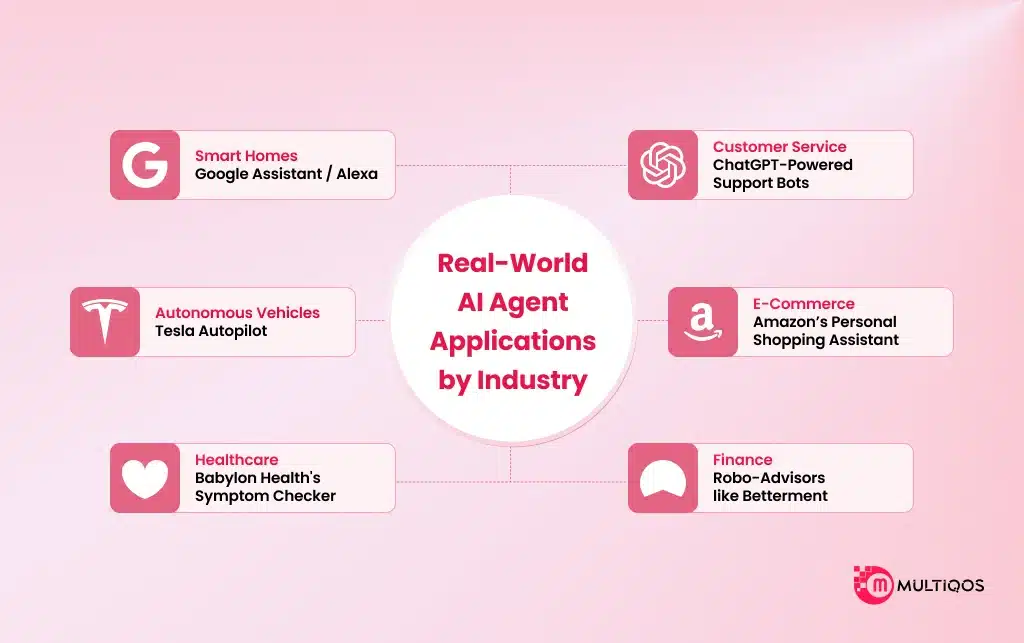
1. Customer Service – ChatGPT-Powered Support Bots
One of the most widely recognized applications is AI-powered support bots. Tools like ChatGPT act as customer service agents that can understand and respond to user queries using natural language processing (NLP).
Here’s how autonomous AI agents work in this context:
- Sensing: They take input via text or voice.
- Thinking: Analyze intent, sentiment, and context.
- Acting: Deliver a coherent response or escalate to a human agent.
This reflects several key characteristics of AI agents: autonomy, adaptability, and environment awareness.
Even though at a first glance they appear to be very similar, there are crucial distinctions between AI agents and chatbots. Whereas chatbots are bound by rule-based flows, AI agents such as ChatGPT are free to adapt, learning from interactions and optimizing responses, attributes that align with the contemporary approach to AI agent development.
2. E-Commerce – Amazon’s Personal Shopping Assistant
Retail giants like Amazon use AI agents to personalize user experiences. The agent collects data on browsing, past purchases, and even dwell time on product pages. Then, it applies learning mechanisms in AI agents, such as collaborative filtering, to suggest relevant items.
The AI agent’s decision-making process evaluates:
- User history
- Real-time preferences
- Current context (e.g., season, cart contents)
This use case showcases goal-driven behavior in AI agents, where the objective is to increase conversions by recommending products the user is likely to buy.
3. Finance – Robo-Advisors like Betterment
In fintech, AI agent development powers robo-advisors that manage portfolios based on client goals, risk tolerance, and market data.
These agents embody components of an intelligent agent:
- Perception: Market trends, portfolio performance
- Reasoning: Portfolio optimization algorithms
- Action: Rebalancing, recommending trade
By automating investment decisions, AI agents reduce the cost of financial planning and improve accessibility.
4. Healthcare – Babylon Health’s Symptom Checker
AI agent development is becoming crucial in diagnostics and telehealth. Babylon Health’s AI symptom checker analyzes user-inputted symptoms and cross-references them with a vast medical database to suggest possible causes or treatments.
Here’s how AI agents interact with environments in this scenario:
- The environment is the user’s health data.
- The agent dynamically adapts its questioning to gather relevant info.
- Then, it suggests next steps (e.g., consult a doctor, take OTC meds).
This real-world AI agent combines reasoning with personalization, exemplifying the benefits of using AI agents in critical fields like healthcare.
5. Autonomous Vehicles – Tesla Autopilot
One of the most complex AI agent examples is the app for self-driving cars. Tesla’s Autopilot uses multiple AI agents to handle tasks such as lane keeping, obstacle detection, and decision-making at intersections.
These agents must juggle reactive vs proactive AI agents paradigms:
- Reactive behaviors: Respond immediately to hazards.
- Proactive behaviors: Anticipate lane merges or adjust speed for traffic patterns.
Autopilot systems reflect the most advanced form of AI agent development, integrating real-time sensor input, high-speed computation, and predictive modeling.
6. Smart Homes – Google Assistant / Alexa
Virtual assistants like Google Assistant and Alexa are embedded with AI agents that manage home automation tasks. These include:
- Adjusting thermostats
- Setting reminders
- Ordering groceries
Such agents exhibit:
- Continuous environment monitoring
- Seamless user interaction
- Integration with multiple devices
This highlights the future scope of AI agent development in building interconnected, intelligent ecosystems within homes.
How AI Agents Work: The Inner Mechanics
To understand AI agent development, you need to know the tech that powers them.
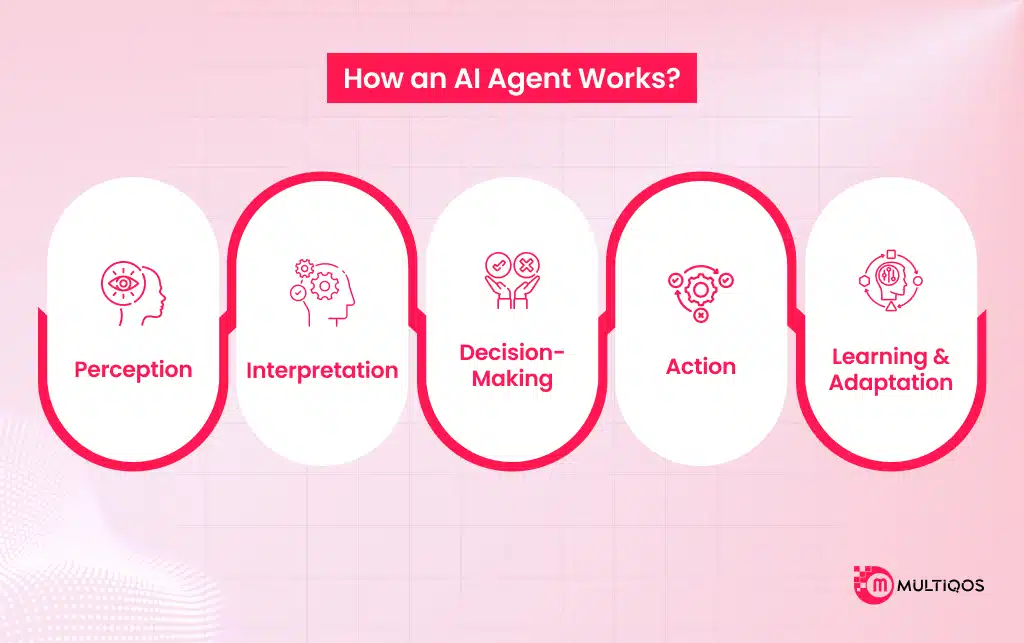
Core Components
Every intelligent agent contains a few fundamental parts:
- Perceptual Input: Sensors or data-gathering modules
- Processing Unit: Where reasoning and decision-making occur
- Action Module: Executes commands in the environment
These together form the components of an intelligent agent.
The Decision-Making Process
The AI agent decision-making process follows this cycle:
- Observe the environment
- Analyze the situation
- Choose an action aligned with the goal
- Learn from the outcome
The process is repeated, continuously improving the agent’s performance—a hallmark of learning mechanisms in AI agents.
Challenges in Implementing AI Agents
While AI agents offer immense value, there are real-world barriers to implementation.
1. Data Sensitivity and Privacy
In healthcare and finance, for example, improperly managed data can lead to severe compliance issues.
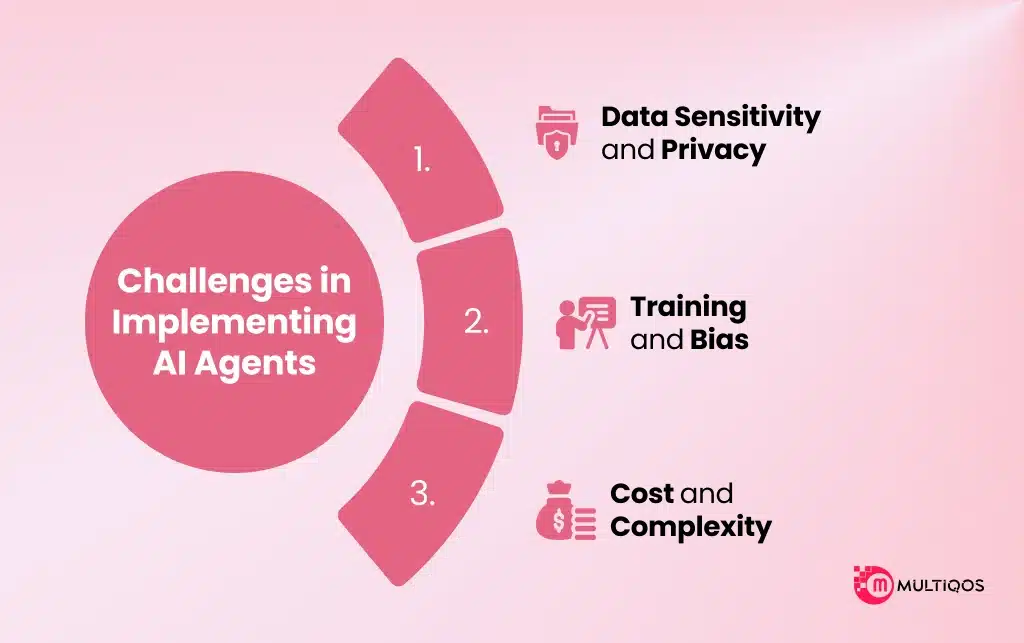
2. Training and Bias
If AI agents are trained on biased datasets, they may reinforce or amplify unfair outcomes. This issue ties directly into challenges in implementing AI agents at scale.
3. Cost and Complexity
Developing robust, autonomous AI agents requires substantial compute power, interdisciplinary expertise, and ongoing support.
The Future of AI Agent Development
As AI matures, we’re moving toward more generalized, intelligent systems capable of handling complex, multi-domain tasks. The future scope of AI agents includes:
- Hyper-personalized virtual assistants
- Autonomous systems in logistics and manufacturing
- Collaborative AI agents for knowledge work
Progress in areas like explainable AI, federated learning, and reinforcement learning will further accelerate the capabilities of these agents.
Conclusion
AI agents aren’t just a theoretical notion — they are active participants in the technology landscape of today. We observe what the development of AI agents means for automation, for intelligence and for adaptivity, from e-commerce to health care.
Let’s recap some key takeaways:
- AI agent definition: Entities that perceive, reason, and act within an environment.
- What does an AI agent do: Collect data, make decisions, and execute actions.
- Examples of AI agents in real life: Chatbots, robo-advisors, smart assistants, and autonomous vehicles.
- Benefits of using AI agents: Increased efficiency, cost savings, and scalability.
- Challenges: Bias, privacy, technical complexity.
- Future outlook: More autonomous, proactive, and versatile AI systems.
But as you look into the world of intelligent systems, this is where understanding these real-world examples is so powerful, because it grounds some of the more abstract theories in what they mean in terms of a practical, and significant AI agent use cases. If you’re a manager product leader or developer, this perspective is vital to navigating the new terrain of AI.
Partnering with a reliable AI ML development company you can take your architecture from concept to production and then scale it out easily - turning your dreams into intelligent, goal-driven systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
A concrete AI agent instance is a system with AI that perceives its environment and takes goal-directed actions. Cases in point: Tesla’s Autopilot (for self-driving), Amazon’s shopping suggestions, and virtual assistants such as Google Assistant or Siri.
If you’re looking to build custom AI agents tailored to your business needs, we’re here to help. Simply contact us through our website to schedule a free consultation and learn more about our AI agent development services.
Chatbots tend to have simple, scripted interactions, whereas AI agents are a type of entity that is intelligent: they can learn, predict, decide, and do things, which provides them with much more powerful functionality.
The future of AI agents includes greater autonomy, integration across platforms, enhanced decision-making, and broader adoption in everyday life—from enterprise tools to personal digital assistants.
Get In Touch






