IoT Payment: How IoT Has Completely Transformed the Modern Payments Market
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Internet of Things
- What Are Internet of Things Payments?
- Difference Between Contactless and IoP Payment Models
- Keeping Payment Data Safe in the IoT
- Ideas for Bringing IoT to the Finance Industry
- How May Payment Service Providers Profit from IoT Payments?
- Technologies to Implement IoT in Payments
- Key Benefits of IoT Payment Solutions
- The Most Promising Types of IoT Payments
- Challenges of IoP Implementation
- Innovative IoT Payment Solution Examples
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT), which was once an abstract notion, is now a palpable worldwide phenomenon. Smart appliances, linked autos, and wearable technology are just a few examples of how the Internet of Things is transforming the ways people interact with their surroundings. And the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand. According to a recent IDC prediction, there will be 41.6 billion linked devices by 2025.
IoT also gives plenty of opportunities for firms in the payments industry to profit from it. The implementation of a concept like the Internet of Things, which essentially allows machines to anticipate demands based on data, argues that customers’ payment experiences can be just as seamless. Also, consumers increasingly want their IoT gadgets to easily integrate payments into their daily lives.
Understanding the Internet of Things
The IoT’s exponential connection is expected to raise payment transaction volumes, establishing a strong payment infrastructure, a critical component for long-term success. Financial firms and other payment service providers can assist companies in preparing for monetization potential by providing complete services that can be integrated into the IoT-enabled quick purchase environment.
It also is worth noting that the IoT’s rapid growth has the potential to increase payment risk and fraud. Banks and other stakeholders must consider the likelihood of rising fraud and create new security methods to authenticate and safeguard customer identities.
What Are Internet of Things Payments?
It’s crucial to comprehend what caused the creation of new payment methods and the trigger that began the aforementioned progress in the world of IoT-based Mobile App Development in USA.
- Consumer Requirements: We, the customers, have become erratic and demanding. We are accustomed to doing everything in the most comfortable manner possible, including shopping. And it is not only since we are picky. Instead, it is because we are just too busy and don’t mind handing over certain minor duties to computer algorithms (and conducting verified transactions is one of those tasks).
- Business Requirements: Consumers’ requirements lead to the needs of the businesses that service them. A disappointed customer is unlikely to become a paying customer in the end. As a result, if a customer wants access to an IoT payment platform, the firm must do everything possible to give it.
- Internet Access: Internet access that is available to everyone. Previously, the Internet was only available to the elite, or the selected few, but today it is available to everyone. It’s time to take advantage of the new possibilities.
- Affordability: The smart system implementation stage is still costly, but it is becoming more inexpensive every year.
- Ever-changing Technology: The unavoidable evolution of digital technology, which occurs whether we like it or not.
Difference Between Contactless and IoP Payment Models
By 2025, the worldwide contactless payment industry is expected to reach $2.23 trillion, an astounding figure in and of itself. As a result, this is perhaps the greatest moment to approach the problem with the utmost seriousness.
By the way, did you realize that contactless and internet technology payments are not interchangeable concepts?
Contactless Payments
As one might expect, such a transaction does not necessitate physical interaction between the card and the terminal. Furthermore, any smart device with an NFC feature and active payment software, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, rings, key fobs, and other wearables, may be used as a bank card. Many fashion houses are already developing high-tech items that might be used as digital wallets.
Doesn’t it sound like a lot of fun? However, it is not yet true IoT payment solutions.
The Essence of Smart Payment in IoT
Wearables have revolutionized the financial industry, ushering in even more technological advancements. IoT devices in the payments business, in particular, have generated amazing outcomes under one condition: these products must be linked to the Internet. Payments in the Internet of Things, also known as invisible payments, should ideally not require human involvement.
Let’s create a hierarchy of unseen transactions that, in their ideal state, generate payments without the need for human intervention:
• At first, a smart gadget can only provide you with information about the state of your bank account; it is not permitted to conduct any actual financial operations.
• The second step is more akin to IoT payment systems, although human involvement is still possible (but it is significantly reduced). The user is usually required to validate the transaction using biometric authentication or something similar.
• The third level entails smart payments that are automated when specific circumstances are satisfied.
Finally, when transactional operations do not require a human at all, full-fledged IoT mobile payments are possible. Smart gadgets make payments on their own, based on the user’s preferences, needs, and specific instructions (such as financial limits, etc.)
Also Read: Differences Between Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Keeping Payment Data Safe in the IoT
Including many advantages of the Internet of Things, the possibility of a security breach must be considered. With so much data being exchanged across so many devices and objects, it’s only natural for hackers to want to gain access to it.
Many of the billions of connected devices were not designed with PCI compliance in mind. Virtually any connected gadget is a possible point of entry for fraudsters, thus they must be maintained protected. In the realm of payments, all devices must follow the PCI protocol to guarantee that any businesses that send sensitive credit card details do so in a safe manner.
Another major challenge with the IoT is user authentication. What if, in the previous printer scenario, the printer purchases $1000 worth of toner instead of $10 since the account has been hacked?
It is critical to have a better grasp of who may be held responsible for such results. Who can be held liable in the case of a breach if the person who approved the transaction cannot be identified?
Tokens hold the key to the solution. In the Internet of Things, tokens will be king.
Tokenization solutions are being developed particularly for the Internet of Things (IoT) since they will be crucial in avoiding data breaches. User authentication may be linked to the payment token, ensuring mutual authentication and ownership.
Ideas for Bringing IoT to the Finance Industry
Mobile App Development Company in usa have worked on this sector and have come up with viable ideas:
- Car as a means of payment: Consider this scenario: your automobile paying for the gas station, toll road, parking, and so on. Nothing will distract you from driving if you don’t have to step out of the car to make a payment or deal with cash while you’re behind the wheel. All you have to do is provide authorization, and the trades will be completed without your involvement.
- AI-based smart home: A home like this has the potential to completely change the lives of family members. The AI system, for example, can make some of the essential purchases on its own. Let’s say you want to buy food depending on the dietary preferences of your housemates while staying inside your budget. By the way, the IoT payment platform will only place orders from online retailers that are eligible and match the criteria.
- Smart self-service stores: Purchases are made without the need for human interaction. The buyer goes about the store, selecting the items he requires, while the payment is done invisibly and seamlessly.
- Smart Coffee Machine: The coffee maker might potentially be self-service, with payment taking place in the backend, saving the customer’s work and attention.
These are only a few samples of new payment options. In reality, much relies on a person’s or company’s demands as well as the technical skills to execute the plan.
How May Payment Service Providers Profit from IoT Payments?
Payment service providers (PSPs) with the assistance of dedicated developers must make a critical decision as financial networks grow bigger and bolder, crossing borders and spanning various devices.
- Take on every task. Deliver an integrated customer experience and a smooth, secure infrastructure.
- Divide and conquer is an effective strategy. Concentrate on growing and protecting payment infrastructure while outsourcing customer service and other activities to partners.
Divide and conquer may be the far superior option in the aftermath of open banking. It’s because digital businesses that have tried to make cautious advances into payments are fully aware of the regulatory challenges. At some time, Amazon, Uber, and Apple all formed ties with banks and payment service providers.
Building a payment infrastructure from scratch makes little sense for most players because there are already a plethora of payment services on the market that are well-liked by customers. When these two prerequisites aren’t satisfied, or when financial institutions don’t care about innovation, digital businesses are more likely to enter the payment industry.
Payment service providers must work on making access to their infrastructure simple, secure, and economical to maintain a competitive advantage in the IoT payment market.
Technologies to Implement IoT in Payments
Although this article will not be able to mention all of the technologies necessary, this section will focus on the ones which are used most often by professional ios and android developers.
- Big Data: The Internet of Things entails continuous data collecting and processing, and since there is so much of it, the notion of Big Date emerges. The Internet of Things collects information on the condition of devices (such as on/off mode), their position, people’s mobility, and more. The data is then sent to a central system, processed, and put to good use (say, to automate some routine tasks). Although financial transactions constitute a minor element of the Internet of Things, they are nonetheless linked to the constant processing of massive data.
- AI & Machine Learning Technologies: Of course, without the utilization of AI technology, there is little prospect of success. After all, the IoT payment platform is supposed to make autonomous judgments, start transactions, which implies it must have intelligence. Furthermore, AI entails the use of machine-learning models. Again, Big Data is implicated: sensors gather data, the central system analyses it, as well as the system learns and improves over time.
- Blockchain: As the name implies, blockchain is a chain of blocks. These blocks are distributed to the system’s reliable members. The lack of third parties and transaction dependability result in decentralisation, immutability of chain linkages, and uncontrollability by any regulatory authority. This is why IoT payments should be implemented via blockchain.
- Tokenization: Tokenization is also linked to and based on the blockchain idea. When it comes to payments, why do we need tokenization? Contactless transactions imply the utilization of card data. And if the gadget that assists in making a payment is susceptible, there is a chance that this information may be stolen. Tokenization substitutes the user’s actual card number with a one-time-use code (token), which can only be used once.
Each successive operation necessitates the creation of a new (also unique) token. As a result, if a fraudster intercepts information about a token during the transaction process, nothing terrible will happen because the token already has done its job as a one-time code. As a result, we safeguard IoT payments and improve their reliability.
Key Benefits of IoT Payment Solutions
Let us look at the benefits served by a team of dedicated developerswith IoT Payment solutions to both consumers and business:
Consumer Perspective
- Decreased transaction time making payments nearly imperceptible to the user
- Greater comfort as user interaction is limited and comfort level is high
- Improved financial habits as The Internet of Things method teaches consumers how to spend money effectively while staying within their budget constraints.
- The rationale is straightforward for the IoP system will carry out the instructions given to it and digital algorithms are not influenced by external factors
- It cuts off the hassle of physical touch, which is essential in the current global pandemic.
Business Perspective
- Offers are tailored to the individual which allows analysis of User activity using big data and AI technologies, and buyers can receive the best-priced offers.
- Increased purchasing activity ensures that the less often individuals use paper money, the more they spend (it appears that parting with money in non-cash is simpler).
- Increasing the speed with which financial transactions are processed due to the invisibility of payments
- Increased corporate efficiency as a result of all of the above.
The Most Promising Types of IOT Payments
The development of IoT payments is well underway. To be precise, their adventure has only just begun, thus the plans outlined below are primitive and incomplete. To turn the dream (IoP) into reality, there is indeed a lot of work to be undertaken.
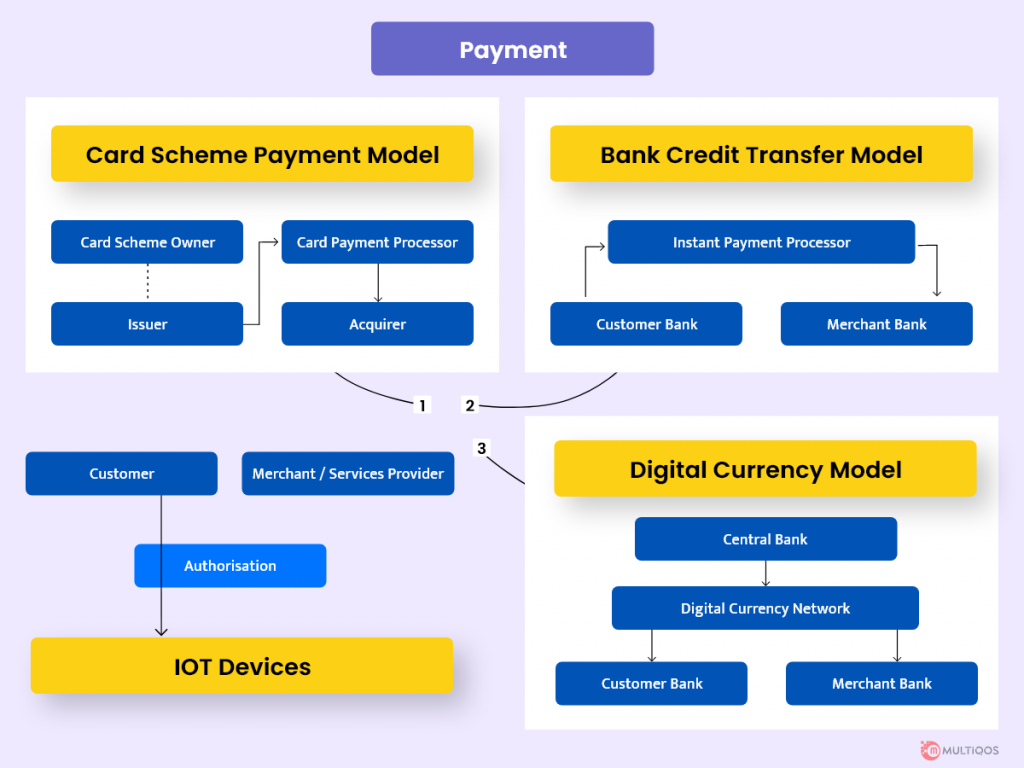
NFC-based Model:
NFC stands for Near Field Communication and is a seamless payment system. When using the NFC model, information is exchanged without direct touch, that is, at a short distance between particular devices, such as a bank card and a terminal. As a result, there is no genuine physical interaction. Magnetic induction is used to read the data.
You might be wondering what IoT mobile payments have to do with it! It’s quite straightforward: With NFC technology and tokenization, practically any gadget may be turned into a type of bank card. Simply inserting a token-based card in the object can turn it into a payment method.
PIS Model:
You have most likely heard of instant payments. It’s an excellent choice if you need to send money to a friend, or family in another country, regardless of their location. The program, similar to SEPA in Europe, simplifies, streamlines, and standardizes the financial process. It’s conceivable because the EU’s PSD2 law lays the groundwork for open banking. As a consequence, with the customer’s agreement, trusted third parties have access to financial information about the bank’s client.
PSD2 spawned the notion of PIS (Payment Initiation Service), which allows providers to handle payments on behalf of customers, such as enabling them to buy something online, transfer money, and so on. Furthermore, IoT in payments might be implemented via PIS-based schemes.
Crypto-currency Model:
The ability to perform monetary operations without the involvement of third parties is implied by crypto-currency and the distributed ledger. Digital money and distributed ledger, as many feels, might be an excellent foundation for developing IoT payment services. Although it is impossible to predict what the bitcoin strategy would yield right immediately, some rules may be required, as well as the involvement of financial regulators. In any event, the model looks to have a lot of potentials.
Challenges of IoP Implementation
Just like advantages, IoP implementation brings along numerous challenges too.
Consumer Conservatism:
Although there is a need for IoT payment solutions, the benefits are apparent. Not everyone, particularly the older population, is ready to accept change. Fear of novel technology, skepticism of digital algorithms, the habit of paying with cash, or a natural worry about the security of IoT payments all contributes to their unease. Users’ worry and distrust, on the other hand, will go away over time as new technologies demonstrate their efficacy and acceptability.
Security Concerns:
Security and data protection issues are the most pressing concerns with smart payment in the IoT. Unfortunately, Internet of Things devices is prone to a variety of cyber-attacks and present new chances for data theft, which cybercriminals are eager to exploit.
On the other hand, implementing an IoT system allows for a more thorough examination of the user, his behavior, habits, and payment history, and, as a consequence, the creation of a realistic portrait of him. And if this person does anything unexpected that is completely out of character for him, there will be a chance to stop fraud before it does significant harm. However, this challenge can be dealt with authentication which can be done in two aspects:
- Authentication of the device
- User authentication
Compatibility with Services, Systems, or Devices:
As payments in the IoT are a new sector, uniform, internationally accepted standards have yet to be defined; yet, their development is something to anticipate. Otherwise, we risk encountering a situation in which certain software fails to function correctly with a specific device. In other words, there is no trust in the interoperability of diverse firms’ digital goods. To remedy the problem, all that is required is a discussion and documentation of the norms that IT developers and device makers must follow.
Imperfectly Optimized Algorithm:
Since the IoT’s relationship to the banking industry is still in its early phases, we may expect a slew of mishaps that will be eradicated over time. Obstacles are a natural part of both people’s and digital systems’ development and advancement. And IoT payment development is no exception. The potential risks and perils, on the other hand, aren’t a valid excuse to reject innovations, which will inevitably benefit all parties involved.
Also Read: The Guide to IoT Development: How to Build an Internet of Things Application
Innovative IoT Payment Solution Examples
- NatWest’s voice banking was launched in 2019 with the support of Google Assistant. The feature operates on a very basic level, allowing you to access information on your savings account and nothing else.
- Amazon Go, which makes shopping more convenient. The consumer is authorized at the store’s entry using the Amazon Go smartphone app on this platform. The program allows payments in an IoT context, works in the background, and uses RFID tags and video cameras to follow the buyer’s purchases. When a product is selected from the shelf, it is added automatically to the shopping list, and payment is completed without interruption.
- Samsung’s smart refrigerators are based on software provided by MasterCard. These freezers are programmed to not only regulate the temperature of the products but also to place orders for meals.
- OpenTable demonstrates an overview of how IoT mobile payments are being used in the restaurant industry. The purpose of OpenTable is to make transactional operations as simple as possible.
Conclusion
From smart speakers to intelligent sensors, smart automobiles to smartwatches, the Internet of Things is poised to become the contemporary consumer’s ubiquitous, omnichannel network. The Internet of Things (IoT), which is becoming more pervasive, has the potential to change the financial sector in the same way that credit cards did. With the help of a Mobile Application Development Company in india, even you can get an IoT solution for your payment app.
Let’s Create Big Stories Together
Mobile is in our nerves. We don’t just build apps, we create brand. Choosing us will be your best decision.
FAQ on IoT Payment
The Internet of Things is used to collect real-world data and act on it according to predetermined rules. Track your heart rate, for example, and upload it once a day. Machine learning creates its own rules based on vast data to enhance its performance over time. Predictive analysis for patient health, for example, before an emergency occurs. This has the potential to save lives and save healthcare expenses.
The number of IoT devices is rapidly increasing which expansion necessitates improved network asset audits. This information covers the device type, software version, network permissions, and device maintenance instructions. Conduct Threat monitoring and testing regularly in networks, and close network ports. For all IoT devices, emerging cybersecurity threats and appropriate actions must be addressed. For security reasons, IoT Edge Computing is being designed to be self-updating.
Get In Touch